Thermography Test and Its Role in Industrial System Inspection
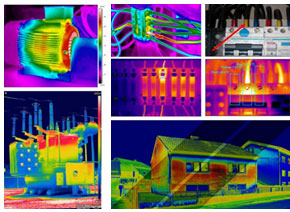
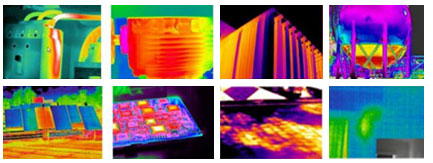
Thermography is a non-destructive method used in technical inspections of industrial systems to detect thermal anomalies in parts and equipment. It is one of the most important methods for detecting defects in the industry.
Technical Inspection
Technical inspection has various definitions in different standards. However, according to ISO 8402, technical inspection and monitoring involve measuring and testing one or more quantities and comparing monitored values with standard values. If there is a discrepancy, the cause is investigated. The most effective form of technical inspection in industrial systems is non-destructive testing (NDT). Among the essential NDT techniques is thermography, also known as thermal testing, which utilizes thermal cameras or thermovision.
Using Thermography Test for Industrial System Monitoring
Thermography, also known as thermovision testing, is a useful tool for monitoring the status of various industrial systems such as electrical, mechanical, and process systems. In case of any faults or errors, the industrial system repair and maintenance unit can fix them promptly.
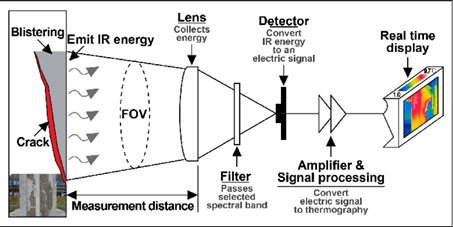
During a thermography test, a thermovision camera is used to capture the heat produced by objects. This heat is emitted in the form of electromagnetic waves that cannot be seen by the naked eye. Special sensors are used to convert this heat into an image with a thermal spectrum, which can be viewed on the camera screen.